Nightly release
This guide is for the unstable nightly release, for the latest release go here.JWT Authorization Grant
Guide for the JWT Authorization Grant specification RFC 7521 / 7523.|
JWT Profile for Oauth 2.0 Authorization Grant is Preview and is not fully supported. This feature is disabled by default. To enable start the server with |
This guide defines how a JWT Bearer Token can be used in Keycloak as an authorization grant. This feature allows clients to send a JWT assertion to request an access token when the client wants to use an existing trust relationship without a direct user-approval step at the authorization server. The assertion is validated solely through the semantics of the JWT (its claims and signature). The trust relationship usually refers to another Identity Provider server (another OIDC server), and allows to obtain a cross-domain or cross-realm access token. In this sense, it is similar to the external to internal request in token exchange V1 (see Configuring and using token exchange for more information).
The JWT Authorization grant is specified by two different RFCs.
In short, the JWT Authorization is an OAuth extension grant as defined by OAuth 2.0 RFC 6749 that is sent to the token endpoint. The grant_type request parameter must be urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. The assertion must be a single JWT with some claims that will be validated by the server. The parameter scope is optional and maintains the same meaning described by Oauth 2.0 and managed by Keycloak for other grants. If the assertion token is valid for authorization, an access token is returned to the client without any interaction to the authorization endpoint.
The trust relationship in Keycloak is defined by an Identity Provider. Currently two Identity Provider types can manage JWT authorization grants:
-
OpenID Connect v1.0 / Keycloak OpenID Connect
-
JWT Authorization Grant
OpenID Connect v1.0 (also the Keycloak OpenID Connect which is just an extension of the previous type) can be used to define a trust relationship with an external OpenID Provider or OP (an OAuth 2.0 Authentication Servers implementing the OpenID Connect specification). This is the common choice. The received assertion will be processed using the provider configuration to validate the JWT token in terms of claims and signature.
The JWT Authorization Grant is a new type of Identity Provider in Keycloak to represent a generic trust relationship. Similar to the previous type, its configuration allows to validate the assertion and obtain an access token using the JWT authorization grant.
Keycloak requires the sub claim in the assertion to be the user identifier in the external provider. The Keycloak user should be previously linked to the Identity Provider. This way there is a link between the external and the internal user ID.
The exact processing that Keycloak performs over the assertion is the following (check the mentioned RFCs for more details about what requirements are needed in the assertion JWT):
-
The requester client should be configured to allow JWT authorization grants.
-
The claim
iss(issuer) should identify the the Identity Provider (issuer configuration option). -
The Identity Provider should be configured to allow JWT authorization grants and the client should be configured to allow exchanging grants with this IdP.
-
The claim
sub(subject) should identify the user in Keycloak. As commented, thesubclaim needs to be the ID of the user in the external provider. The user in Keycloak should be linked to the Identity Provider. The linking information will finally locate the user in Keycloak. -
The claim
aud(audience) should identify the Keycloak server (issuer or token endpoint URL). -
The claim
exp(expiration) should be present and validated. -
Other claims like
nbf(not before),iat(issued at) andjti(JWT ID) can be present and should be validated in that case. -
The JWT should be signed and its signature should be verified with the keys associated to the identity provider in Keycloak.
Configuration
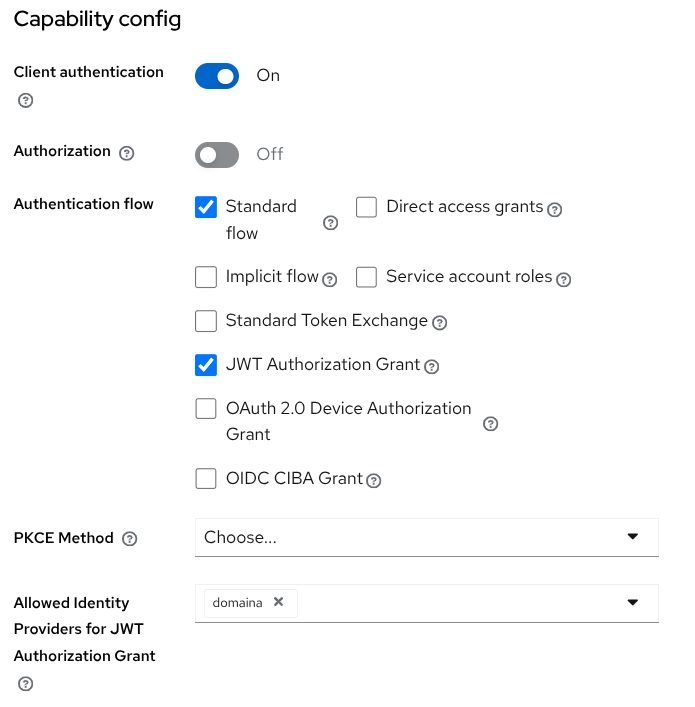
Only confidential clients can request a JWT authorization grant. In order to allow a client to send such a grant, the client should be configured accordingly. Using the admin console, clients → select your client → Settings tab → Capability config section.
-
Enable the JWT Authorization Grant capability.
-
In the option Allowed Identity Providers for JWT Authorization Grant, select all the Identity Providers that this client can use for authorizing grants.

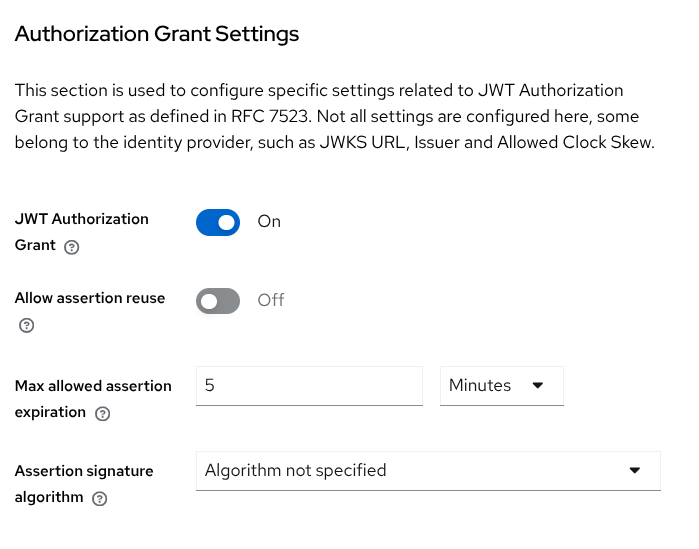
The Identity Provider (both types commented in the introduction) needs to also be configured to establish the relationship that will validate the assertion. In Identity providers → select your OIDC or JWT provider → Settings tab → Authorization Grant Settings section.
-
Enable the option JWT Authorization Grant switch.
-
Configure the rest of options as desired.
-
Allow assertion reuse: By default Keycloak only allows one-time assertions (re-using is not permitted) and the the
jticlaim should be present in the JWT (unique identifier of the token). -
Max allowed assertion expiration: The maximum expiration the server will allow in the assertion. Default 5 minutes.
-
Assertion signature algorithm: The signature algorithm that is valid for assertions. If not specified any signature is valid.
-
Allowed clock skew: Clock skew in seconds that is tolerated when validating identity provider tokens. Default value is zero.
-
Limit access token expiration: If enabled the access token lifespan will be limited to the expiration of the JWT assertion but only if the JWT assertion expiration is less than the calculated access token expiration.
-
| The OpenID Connect Identity Provider types have one extra configuration switch Allows Client ID as audience for assertions, placed in the Advance settings section. This option, when enabled, sets the the Client ID of the provider configuration as the only valid audience for assertions used in Federated client authentication and in JWT Authorization Grants. The client ID is used instead of the token-url/issuer-url defined in the respective specifications. This behavior is not covered by any standard. |
Besides the previous specific options, both identity provider types need some basic configuration related to assertion and signature validation.
-
Issuer: Issuer for the assertion. Required.
-
Use JWKS URL: Whether a JWKS endpoint URL is used to obtain the keys that will validate the assertion signature. If disabled, the keys should be provider manually by the administrator. The recommended value is On.
-
JWKS URL: The URL for downloading the signing keys. Required if Use JWKS URL is enabled.
-
Validating public key id: Fixed
kidfor validating assertion signatures. This option can be left empty to just validate the signature with the configured public key. This option can only be specified if Use JWKS URL is disabled and the validating key is defined as a fixed key in PEM format. -
Validating public key: The public key in PEM or JWKS format that must be used to verify external IdP signatures. Required if Use JWKS URL is disabled.
| When JWT Authorization Grant is configured with the OIDC Identity provider, the signatures on the JWT tokens sent to the token endpoint are always validated. The OIDC identity provider option Validate Signatures is ignored for the JWT Authorization Grant as it is used just for validation of the signatures on the tokens retrieved from the OIDC identity provider during authentication of the users with this OIDC identity provider. |
Examples
This is an example request for the JWT Authorization grant that is sent to the token endpoint. The client ID is test-client, it uses a secret to authenticate, and it is configured to allow JWT Authorization Grant to an Identity Provider whose issuer is https://jwt-idp.example.com.
POST /realms/demo/protocol/openid-connect/token HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Accept: application/json
client_id=test-client&
client_secret=XXXXX&
grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&
assertion=eyJhbGci[...redacted...].eyJpc3Mi[...redacted...].J9l-ZhwP[...redacted...]The important parameter is the assertion. Below is an example JSON object that can be encoded to produce the JWT Claims Set used inside the assertion.
{
"jti":"abcd1234-5678-efgh-ijkl-9012mnopqrst",
"iss":"https://jwt-idp.example.com",
"sub":"b3588c7e-14cb-46a9-9387-28adfd82f7a4",
"aud":"https://keycloak.server/realms/demo",
"iat":1764839065,
"exp":1764839365,
"other-claim":true
}Note the claims should contain iss that identifies the Identity Provider, sub that contains the user ID in the external system that will locate the Keycloak user using the link to the provider, aud should be Keycloak’s issuer or token endpoint, jti guarantees one-time use, and exp is mandatory. Other claims can be added to the token.
The previous JSON example should be signed and the JWT header should specify the algorithm and the key identifier used to sign it. That key needs to be correctly configured in the Identity Provider (via JWKS URL or manually) to validate the signature.
{"alg":"ES256", "kid":"2AOACLJmd5dQ8HPrDxwpkS-83yBhrzaLWSny9wmnYcY"}Keycloak will validate the request and assertion. If everything is correct, the response will contain an access token ready to be used.
{
"access_token":"eyJhbG[...redacted...].eyJleH[...redacted...].RFnNEv[...redacted...]",
"expires_in":300,
"refresh_expires_in":0,
"token_type":"Bearer",
"not-before-policy":0,
"scope":"email profile"
}| Following the spec recommendation, the JWT Authorization Grant never issues a refresh token and a transient session is always created. The access token can be used normally in Keycloak through the introspection, user-info or any other endpoint. It will be valid until expired or explicitly revoked by the revocation endpoint. |
How to get a valid token for JWT Authorization Grant
The JWT Authorization Grant feature needs a previous JWT assertion in order to be exchanged for an access token. We can name the external OpenID Connect Provider (OP) domaina, the one that is represented in Keycloak via the Identity Provider. And we can name the Keycloak server that receives the JWT authorization grant domainb. The domaina should somehow issue a JWT that is a valid assertion for domainb.
If domaina is a server different to Keycloak, we don’t know how that initial JWT is obtained. But note that the specification enforces some processing of the assertion to be valid and return the access token. The way the client gets or generates such a JWT assertion in domaina depends completely on domaina server and client.
In case the external identity provider is another Keycloak server or realm, Standard Token Exchange can be used to obtain such a token (see Configuring and using token exchange for more information). When both sides are Keycloak realms, the idea can be summarized in two basic points:
-
For
domaina,domainbis an audience that can be restricted via token exchange. -
For
domainb,domainais an Identity Provider that is used to validate the assertion. The user indomainbis also a valid user previously linked todomainavia the identity provider.
See OAuth Identity and Authorization Chaining Across Domains for a detailed configuration to perform authorization chaining across two Keycloak realms.
Client policies and JWT Authorization Grant
New conditions and executions related to JWT Authorization Grant have been added to clients policies in Keycloak.
-
Condition identity-provider-alias. This condition allows to select requests that involve a specific identity provider alias. A list of aliases can be defined, and the condition evaluates to
trueif one of the Identity Provider in the list is present. For the moment the condition only manages the JWT Authorization Grant but can be extended for future operations that involve Identity Providers. -
Executor downscope-assertion-grant-enforcer. The executor enforces requested scopes to not exceed the scopes included in the assertion token (claim
scopein the JWT). If a scope is requested that is not already present in the assertion, an error is returned. This executor should be used to prevent getting more privileges (scopes or audiences) than the ones granted in the initial assertion JWT (only downscoping is permitted).The enforcer can be used for any request that uses an assertion parameter. Currently it is used for
assertionin the JWT Authorization Grant andsubject_tokenin Standard Token Exchange. -
Executor jwt-claim-enforcer. This executor allows to configure extra requirements for claims in the JWT assertion token. For example, if we want the assertion to contain an
iatclaim or a custom claim with a specific value. The configuration allows us to set any claim name and any claim value (using a java regex). If the claim in the JWT assertion does not match the regex, the request does not proceed and an error is returned.As the previous executor, for the moment this enforcer can be used for JWT Authorization Grant and the Standard Token exchange.
-
Executor jwt-authorization-grant-audience. The executor allows to configure different and exclusive valid audiences for the assertion. The JWT Authorization Grant processing ensures, by specification, that the audience of the assertion is the Keycloak issuer or token endpoint URL. You can also use the Client ID as valid audience (option Allows Client ID as audience for assertions) for the OpenID Connect identity providers. Using this executor, you can configure one or more valid audiences instead of the default ones for the requests processed by the client policy.
The jwt-authorization-grant-audience executor changes the validation of the assertion audience out of the standard compliance. This behavior can have major security implications.